AOP (Aspect Oriented Programming) 切面導向設計
是一種程式設計的模式,主要理念是為了減少重複出現的邏輯 ,比方說 log 紀錄,登入驗證、資料驗證等重複性事務,如果多個方法都需要執行到這類方法,就可以抽出來透過定義在切面中,減少程式耦合及方便去進行維護,讓開發者可以專注在更重要的業務邏輯中。
如同下圖每個箭頭是不同的方法或流程,如每個方法都要加入同樣的處理,就可以當成一個切面抽出來所以像是 log, security 的部分就被稱為 cross-cutting concerns 但都可以抽出共同需要處理的部分作為切面(藍色及綠色)。
SpringBoot 本身也提供好用的註解去實踐這樣的設計模式,可以進行切面的操作,你可以根據切入點的執行前中後等等進行設定,以控制我們的方法執行的順序。
Spring AOP 使用 定義切面
通常要使用 Spring Boot AOP 需要先將切面定義出來,會在我們需要標記的切面類別上加上 @Aspect,且注意需要加上@Component 將類別標記成為 bean 才可以使用
1 2 3 4 5 6 @Component @Aspect public class LogAspect { }
把需要的東西注入及標註哪些方法需要被 @Pointcut 標記為切入點套用切面
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 @Component @Aspect public class LogAspect { private final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(this .getClass()); @Pointcut("execution(* com.example.demoaop.TestController.*(..))") public void pointcut () { } }
Execution 切入點 關於切入點 execution 表達式:
切入點為 com.example.demo.Test 底下的 print() 方法
execution(* com.example.demo.Test.print())
切入點為 com.example.demo.Test 底下的所有方法
execution(* com.example.demo.Test.*(..))
切入點為 com.example.demo 這個 package 中的所有 class 的所有方法(不包含子 package)
execution(* com.example.demo.*(..))
切入點為 com.example.demo 這個 package 及其底下所有子 package 中的所有 class 的所有方法
execution(* com.example.demo..*(..))
Advice 切面控制 控制切面的執行被稱為 Advice ,Spring 有提供 5 種 Advice 可以讓你操作方法需要執行的時間
@Before : 在切入點執行前前執行切面。@After : 在切入點執行後後執行切面。@AfterReturning : 在切入點傳回(return)內容後執行,可以對傳回內容進行一些加工處理。@Around : 在切入點前後執行切面,並配合 proceed 可控制何時執行切入點本身的內容。@AfterThrowing : 當切入點拋出例外後執行
範例及應用
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 package com.example.demoaop;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;import java.io.IOException;@RestController public class TestController { @GetMapping("/test/{word}") public String test (@PathVariable String word) throws IOException { if (word.equals("yes" )) { throw new RuntimeException (); } return word; } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 package com.example.demoaop;import org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint;import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.*;import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;import org.slf4j.Logger;import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;import java.util.Arrays;@Component @Aspect public class LogAspect { private final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(this .getClass()); @Pointcut("execution(* com.example.demoaop.TestController.*(..))") public void pointcut () { } @Before("pointcut()") public void before (JoinPoint joinPoint) { System.out.println("*****before advice start*****" ); logger.info("do before " + joinPoint.getSignature().getName()); Arrays.stream(joinPoint.getArgs()).forEach(System.out::println); System.out.println("*****before advice end*****" ); } @After("pointcut()") public void after (JoinPoint joinPoint) { System.out.println("-----after advice start-----" ); logger.info("do after " + joinPoint.getSignature().getName()); System.out.println("-----after advice end-----" ); } @Around("pointcut()") public Object around (ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable { System.out.println("=====Around advice starts=====" ); long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); Object result = joinPoint.proceed(); long spentTime = System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime; logger.info(joinPoint.getSignature().getName() + " Time spent: " + spentTime); System.out.println("=====Around advice ends=====" ); return result; } @AfterReturning(pointcut = "pointcut()", returning = "result") public void logReturnResponse (Object result) { System.out.println("=====after returning advice starts=====" ); if (result != null ) { System.out.println(result); } System.out.println("=====after returning advice ends=====" ); } @AfterThrowing(pointcut = "pointcut()", throwing = "throwable") public void afterThrowing (JoinPoint joinPoint, Throwable throwable) { System.out.println("=====after throwing advice starts=====" ); System.out.println(joinPoint.getSignature().getName()); System.out.println(throwable); System.out.println("=====after throwing advice ends=====" ); } }
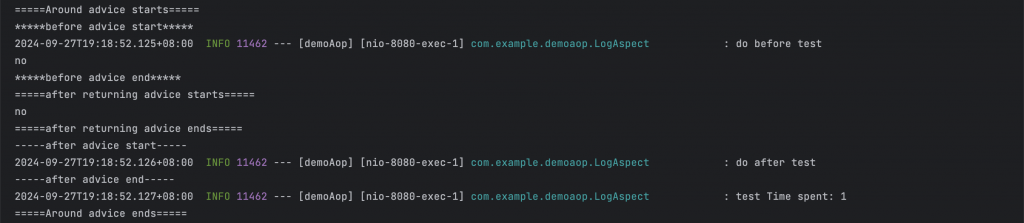
如果當我啟動後並且透過 TestController 的 test 方法進行請求並帶入 “no”,就會看到以下 log 顯示
around start ->
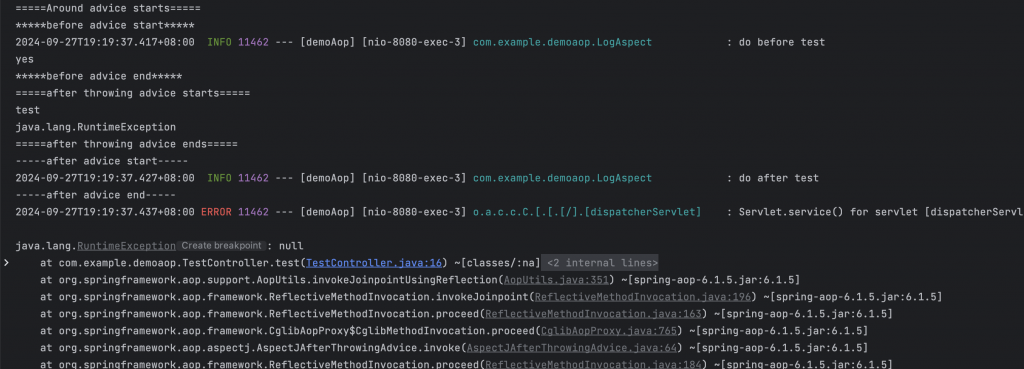
如果是請求帶 yes 導致中途拋出異常就會變成
around start ->
*after 不管有沒有拋錯都執行
所以這就是基本 AOP 的用法,大家應該對於相關的切面控制都有一定的了解了,不妨可以嚐試加入自己的專案內,針對一些特定位置重複會進行的方法或是 log 紀錄抽出來作為切面,這樣設計可以讓程式碼更加簡潔。
參考資料:
【Spring Boot】第 20 課-切面導向程式設計(AOP) 使用 Spring AOP Spring Boot 零基礎入門 (12) - Spring AOP 的用法